
Introduction:
Ad density refers to the percentage of visible space occupied by the ads on the web page.
More ads on a page (higher ad density) can make the screen look messy and hide the content and also impact on page load time and user engagement. Having fewer ads (lower ad density) makes the page cleaner and easier to use but the side effect is we see potential drop in revenue. This creates a very crucial question for publishers, How can we achieve optimal revenue with preserving user experience?
Rules for Ad density Calculations:
To ensure a balanced user experience and maintain viewer engagement, the ad density on a webpage is often restricted to adhere to a 30% rule. This guideline dictates that the cumulative area occupied by ads should not surpass 30% of the total page area. In practical terms, this means that if a webpage has a height of 1000 pixels, the total height of the ads displayed should not exceed 300 pixels.
To calculate ad density, we focus on the pixel measurements of both the ads and the entire webpage:
- Ad Unit Area: This is the total area covered by all the ads on the webpage, calculated by multiplying the height and width of each ad unit and summing up the results.
- Page Area: This represents the entire area of the webpage, calculated by multiplying its height and width.
Example:
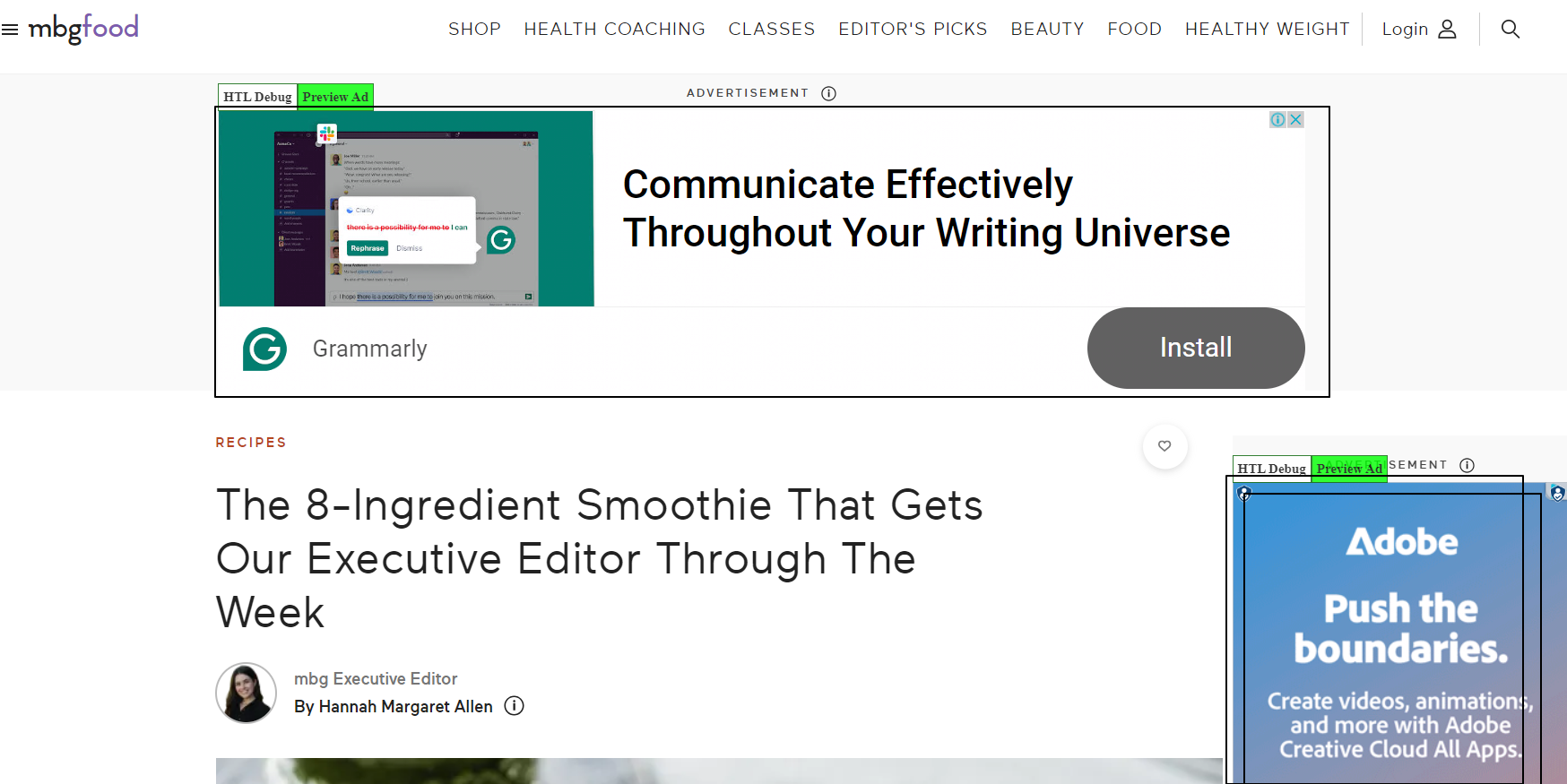
Given a webpage with a viewable area of 728 pixels in height and 1500 pixels in width, and two ad units with the following dimensions:
Ad Unit 1: Height (970px) x Width (250px)
Ad Unit 2: Height (300px) x Width (250px)
We calculate the total ad area by summing the individual areas of each ad unit:
Total Ad Area = (970px * 250px) + (300px * 250px) = 242,500 square Px+75,000 square Px= 317,500 square px
Next, we calculate the total page area:
Total Page Area = 728px * 1500px = 10,92,000 square pixels
Finally, we determine the ad density:
Ad Density = (Total Ad Area / Total Page Area) * 100% = (317,500 sq px / 10,92,000 sq px) * 100% = 29.02%
Consequences of High Ad density:
High Ad density on web pages can have several significant consequences that affect user experience, website performance and advertiser effectiveness.
- Poor User Experience
- High Ad density can move users away from the site. Ads may obstruct the view, disrupt reading flow and lead to bad. This can result in higher bounce rates and decreased user engagement.
- Reduce Content visibility
- Excessive ads can obstruct the main content of a webpage. Users may struggle to find the information they are looking for.
- Slow Page Load Times
- Ads often require additional resources to load, including scripts, images, and tracking codes. High ad density increases the number of these elements, resulting in longer page load times.
- Negative Impact on SEO
- Search engines prioritize user experience when ranking of the website occurs. Pages having high ad density receives low ranking due to high bounce rate.
Factors Influencing Ad Density:
- Ad Format:
- The format of advertisements plays an important role in determining ad density. Some formats, such as banner ads or text ads, may allow for higher densities compared to video ads.
- Content Relevance:
- Ad density depends on the contextual ads. The ads related to content related ads having more ad density as compared to non-contextual ads.
- Advertiser Demand
- More demand for advertisers leads to more ad density while lower demand leads to lower ad density.
- Regulations and Policies:
- Regulatory restrictions and platform policies can also influence ad density.
- Competition:
- Competition among advertisers for ad slots can drive more ad density. If there is more competition in the advertiser for a specific publisher, the publisher tends to have more ad slots on that page.
Industry Standards:
- Digital Display Advertising:
- Websites – Ad density on the websites should be in the range of 20% to 30% of the total page space.
- Mobile Apps – Ad density on mobile apps should be less than Ad density on websites due to limited space on mobile screen. It should be 20% of total page space.
- Television Advertising:
- In television advertising, ad density is regulated by the duration of commercial breaks. Television advertising depends on the duration of the shows.
- Print Advertising:
- Ad density in print advertising depends on layout of page and editorial content. Magazines have generally high ad density as compared to newspapers due to niche audiences.
- Social Media Advertising:
- Social media platforms like Facebook and Instagram may display multiple ads on the user reels and feeds in the form of text ads and during scrolling the reels we will see the ads.
Optimizing Ad Density by data
- A/B testing:
- We can conduct A/B tests of different ad density and placements. After the A/B test we can do impact analysis and check the performance of KPIs like CTR, user engagement and bounce rate.
- Heatmap Analysis:
- Use heatmap tools to visualize user interactions with ad placements on your website or app.
- Ad Performance Monitoring:
- We can monitor the performance of Ads and check the ad density of the individual ads and see the performance.
- Dynamic ad serving:
- Implement dynamic ad serving algorithms that adjust ad density in real-time based on user interactions.
- Ad Format Optimization :
- Based on different ad formats so we can find the most effective ad format for the audience.
Static and dynamic Ad density
- Static ad density: Static ads are the simple ads that don’t change. Advertisers use static ads when he have to create awareness for any brand. Static ads are relatively easy to create and don’t not required any complex programming.
- Dynamic ad density: These ads generate on the base of user behavior on the web page and target very specific users. Dynamic ad density enables advertisers and publisher to optimize site placements.









